CEH 3-Scanning Networks
What is Scanning?
- Scanning is a process of identifying network and service related information by communicating with the target.
- Scanning helps in identifying IP/Host-names, Ports, Services running on ports, Live hosts, Vulnerable services running on the target network.
Types of Scanning:
Network Scanning:
Identifying the number of computers on the network.- Ping Sweep
- Arp Scan
Port Scanning:
Listing open ports and services running on those ports.- SYN Scan/Stealth Scan/Half-Open Scan
- TCP Connect Scan
- ACK Scan/Firewall Detection Scan
- XMAS Scan
- FIN Scan
- NULL Scan
- OS Detection Scan
- Script Scan
- UDP Scan
- Service Detection Scan
1. Network Scanning:
- During the network scanning process, attackers gather a list of IP addresses of computers that are live on the target network.
- The job of the attacker will be easy if he/she can analyze the network structure and services running on each machine.
List of Network Scanners
- Angry IP Scanner
- Advanced IP Scanner
- Netdiscover
- Autoscan
- hping3
- Nmap
Types of Network Scan:
- Ping Sweep: Technique used to find number of hosts alive in a network by sending a set of ICMP ECHO packets to a network and sees which host responding.
- Arp Scan: The ARP Scan shows all active devices even if they have firewalls, by sending ARP packets to a network.
2. Port Scanning:
Be we going to discuss about port scanning, first we will discuss about what are ports and port numbers.
What Are Ports and Port Numbers?
- Ports are virtual(logical) entry points to any digital device.
- Devices can communicate with one to another using port.
- There are virtually 65535 ports available in every device.
- Those can be identified with port numbers, ranging from 0 to 65535.
- 0 to 1023 Well known ports
- 1024 to 49135 Random ports
- 49136 to 65535 Experimental ports
Port Scanning:
- Port scanning is a technique where the attacker will send communication probes to targets to see how the target is responding to them.
- Based on the response attacker will determine what ports are open and several other port details, like service running on the port numbers, and OS the target is running.
List of Port scanners
- Nmap
- SuperScan
- Strobe
- Zenmap (Available for Windows Also)
Type of Port Scan:
- TCP Connect Scan / Full Open Scan: Nmap directly communicates with the operating system to establish a connection with the target machine and port by issuing the connect system call.
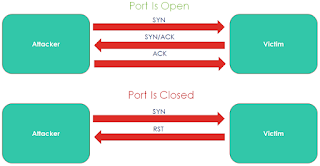
- SYN Scan / Half-Open Scan / Stealth Scan: SYN scan is the most popular scan option. It can scan thousands of ports in a short period on a fast network not hampered by restrictive firewalls.
- ACK Scan/Firewall Detection: This scan is different from others scanning operations discussed before; it never determines open ports. It is used to identify firewall rules, determining the type of firewall and identify filtered ports.
- XMAS Scan: The Xmas-Tree scan sends a TCP packet with the following flags:
- URG: Indicates that the data is urgent and should be processed immediately.
- PSH: Forces data to a buffer.
- FIN: Used when finishing a TCP session.

- FIN Scan: FIN scan, which attempts to close a connection that isn't open. The operating system generates an error if service is not running on target port. If a service is listening, the operating system will silently drop the incoming packet. Therefore, no response indicates a listening service at the port.
- NULL Scan: A data packet with zero flag values will be sent to a TCP port. (In a regular TCP communication, at least one bit or flag is set). In TCP connect / SYN scans, a response indicates an open port, but in a NULL scan, a response indicates a closed port.
Importance of Scanning:
- Scanning will provide an exact outline of the network structure of the target workspace.
- It is beneficial for hacking target servers or individual computers.
- Scanning will provide a blueprint of entire network and details about devices running on the network, information related to network topology and helps in deciding what operating system is running on target computers.
Mitigation:
- Block ICMP and UDP inbound.
- Disable unused ports with support of policy settings.
- Change system and application banners to counter software detection attacks.
- Always use a genuine operating system, update it frequently.
- Use IDS & IPS to detect and prevent attacks.
- Use “duckduckgo” or “StartPage” search engine to protect privacy.






Comments
Post a Comment