CEH 11- Session Hijacking
What is Session?
- A session stores information (in variables) to be used across multiple pages, when a user logs into his online account.
- Unlike cookies, this information is not stored on the user’s computer.
- Typically maintained by the server, and created on the first request or after an authentication process.
- The session-id is exchanged between a web browser and the server on every request.
- Different ways to exchange session-Id:
- Hidden Form fields
- Cookies (most common)
What is Session Token?
- Session ID or session token is a piece of data that is used in network communications to identify a session.
- It is used to determine a user that has logged into a website.
- These session IDs or token can be used by an attacker to hijack the session and obtain potential privileges.
- A session ID is usually a randomly generated string to decrease the probability of obtaining a valid one by means of a brute-force search.
What is Cookie?
- Cookies are strings of data that a web server sends to the browser.
- When a browser requests an object from the same domain in the future, the browser will send the same string of date back to the origin server.
- The data sent from the web server in the form of an HTTP header called "Set Cookie".
- The browser sends the cookie back to the server in an HTTP header called "Cookie".
- The primary purpose of a cookie is to create customized web pages based on user identities.
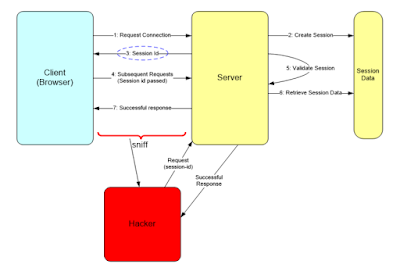
Session Sniffing:
- Attackers can sniff all the traffic from the established TCP session and perform identity theft, information theft, fraud, etc.
- The attacker steals a valid session ID and uses it to authenticate himself with the server.
Session Hijacking:
- Session Hijacking refers stealing of this session-Id and using it to impersonate and access data over a valid TCP communication session between two computers.
- Application level hijacking is about gaining control over the HTTP user session by obtaining the session IDs.
Attack Methods:
- Guessing Session Id
- Session Fixing
- Session Sniffing
- Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
Mitigation:
- Do not click on the links that are received through emails.
- Logout from the application instead of closing the browser.
- Always use an updated browser.
- Clear the browsing data like cache, cookies, etc.
- Create Session keys with lengthy strings or random number.
- Regenerate the session ID after a successful login to prevent session fixation attack.
- Encrypt the data and session key that is transferred between the user and the web servers.
- Expire the session as soon as the user logs out.
- Use firewalls to prevent the malicious content entering into the network.



Comments
Post a Comment