CEH 19- Cloud Computing
What is Cloud?
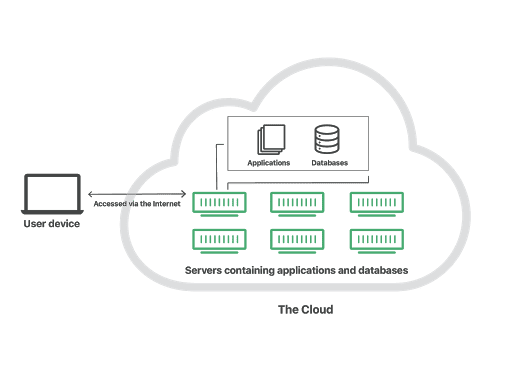
The Cloud refers to Servers that are accessed over the Internet.
The software and databases runs on those servers.
Cloud servers are located in data centers all over the world.
By using cloud computing, users and companies don't have to manage physical servers themselves or run software applications on their own machines.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing is the practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer.
The information being accessed is found in "the cloud" so the user need not to be in a specific place to gain access in which data is stored.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing:
- On-demand self-service
- Distributed storage
- Rapid elasticity
- Automated management
- Broad network access
- Resource pooling
- Measured service
- Virtualization technology
- Pay per use
Cloud Computing Services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a service (PaaS)
- Software as a service (SaaS)
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) provides virtual machines and other abstracted hardware and operating systems which may be controlled through service API.
In these services, cloud service providers install operating system images, and application software’s on the cloud infrastructure based on user’s requirement.
The cloud service provider is responsible for patching and maintains the operating systems and the application software.
Examples: Amazon Web Services, Google Compute Engine, IBM Cloud etc.
2. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS):
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offers development tools, configuration management, and development platforms on-demand that can be used by subscribers to develop custom applications.
Typically it includes a framework that satisfies the requirement of a developer.
The Application developers can take advantage of using the licensed software without worrying about the cost and complexity involved in maintaining the underlying hardware and software layers.
Examples: Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure, etc.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS):
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offers software to subscribers on-demand over the Internet.
CSP (Cloud service provider) manages the infrastructure and platforms that run these applications.
This service eliminates the need for installing and running the applications on the user's computers.
Examples: Google Docs, Calendar, Web-based office applications, etc.
Cloud Deployment Models:
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Community cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
1. Security:
- Less investment in security.
- Better disaster recovery.
- Effective patch management and implementation of security updates.
2. Economic:
- Environment-friendly.
- Less maintenance.
- Less power consumption.
3. Operational:
- Deploy applications quickly.
- Scale as needed.
4. Staffing:
- Less IT staff.
- Well usage of resources.
- Less personnel training.
Cloud Computing Threats:
- Illegal access to the Cloud.
- Privilege Escalation.
- Hardware Failure.
- VM-Level attacks.
- Cryptanalysis Attacks.
- SQL Injection Attacks.
- DoS and DDoS Attacks.
- Session Hijacking using XSS Attacks.
- Loss of Business Reputation due to Co-tenant Activity.
Cloud Security Tools:
Applications: Web App Firewalls, Scanners, Transactional Security.
Information: Strong Encryption, Database Activity Monitoring, DLP.
Network: NIDP/NIPS, Firewall, Deep Packet Inspection, Anti-DDoS.
Trusted Computing: Hardware and Software API's.
Computer and Storage: Host-based Firewall, HIDS/HIPS, Integrity and File/Log Management.
Management: Patch Management, Configuration Management.
Physical: Physical Plant Security, CCTV, Guards.
Mitigations:
- Enforce data protection, backup and retention mechanisms.
- Disclose relevant logs and data to customers.
- Prevent unauthorized server access using security checkpoint.
- Monitor the client’s traffic for any malicious activity.
- Implement strong key generation, stronger authentication management, and destruction practices.
- Check for data protection at both design and runtime.
- Enforce legal contracts in employee behavior policy.
- Prohibit users from sharing application and services credentials.
- Ensure that physical security is a 24 x 7.
- Leverage strong two-factor authentication techniques where possible.









Nice content.....Easy to Understand
ReplyDeleteThank you
DeleteElaborate info.
ReplyDeleteThank you
Delete